The decline of empathy in health professions education has been shown to deteriorate in learners as they progress through their education program. As educators, how do we encourage our learners to maintain their empathy over time? Can we use novel teaching methods to reinforce and strengthen learners’ empathetic skills?
A powerful, and often overlooked, teaching method is role modeling. Role modeling is the process by which educators teach learners by modeling appropriate knowledge and behaviors. Educators who routinely utilize role modeling have been found to demonstrate “the skills, knowledge, and attitudes that comprise a professional identity.”
Utilizing role modeling to demonstrate empathy can have a direct impact on learning and the learning environment. Mikkonen et al. promoted the utilization of empathy and found that empathetic educators promoted caring, learner-centered environments that motivated students to accomplish their learning goals. The establishment of an empathetic learning environment can reinforce the knowledge, skills, and attributes necessary for learners to become successful health care professionals. Additionally, the utilization of empathy as a component in the learning curriculum can reinforce the development of empathetic behaviors in learners.
How can educators reinforce their empathetic role modeling skills?
Reflection is a powerful learning tool for educators to further develop and refine their empathetic and role modeling skills. Reflection is key in the process of incorporating new knowledge, skills, and behaviors. Educators can utilize reflection to examine the role modeling experience and learn from it and utilize the same context in future educational settings.
Reflection on past experiences allows educators to:
- Assess the experiences to extract the knowledge, skills, or attributes which would benefit them most as they developed their teaching skills
- Utilize the experience to create a safe learning environment
- Apply positive experiences to create the learning environment
- Gain understanding of the impact of empathy from positive experiences in which empathy was involved
- Determine what they did not want to model based on prior negative experiences
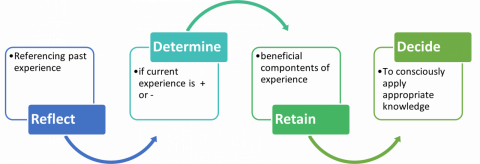
To effectively role model empathy through reflection, educators can model the following steps to their learners as described in the image above:
- Reflect on past experiences
- What occurred during the experience?
- Determine if the experience was positive or negative
- How did you feel during the experience? Was it a positive experience or negative experience?
- Retain beneficial components of the experience to take forward
- What aspects of the experience made an impact on you? Why?
- Decide what aspects of the experience you will apply moving forward?
- What aspects of the experience will you take forward? Or are there aspects of the experience that you will not want to model to others?
The utilization of reflection allows instructors to deepen their understanding of the role they play in educating others, thereby broadening their knowledge, skills, and attributes.
How have you role modelled empathy with your learners? Comment below and join the conversation!
Did you know that the Harvard Macy Institute Community Blog has had more than 325 posts? Previous blog posts have explored topics including reimagining the visiting professorship during a pandemic, personal protective equipment vs empathy, and a peaceful approach to virtual teaching.
Amy Seegmiller Renner, PhD, MS, (Assessment ’20; Leaders ’20) Director of Director of Diversity and Anti-Racism Curriculum in the Office of Education Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion and Assistant Professor at the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science. Amy’s areas of professional interest include inclusion, diversity, equity, anti-racism, empathy, role modeling, and leadership development. Amy can be followed on Twitter.

Elissa Hall, EdD, MA, (Educators ’16; 2.0 ’16; Leaders ’21) is Director of Curriculum and Education Technology and Associate Director of Education Science, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science and Assistant Professor at Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science. She is also Harvard Macy Institute Transforming Your Teaching for the Virtual Environment course director. Elissa’s areas of professional interest include strategic planning, systems design, and implementation of enterprise-wide education initiatives aligned with curriculum, assessments, education technology, and digital pedagogy. Elissa can be followed on Twitter.

HMI Staff


